Low-voltage circuit breaker-MCB.
The EURO standard for MCB is IEC-60947.
What is MCB?
MCB stands for a miniature circuit breaker. The circuit breaker is an electro-mechanical switching device, which plays a key role in breaking and making a circuit, under normal and abnormal conditions.
MCB safely disconnect the circuit at the on-load condition.
Instead of fuses, we can use MCB to protect electrical equipment. The maximum rated capacity of MCB is 100amps and its tripping current is a maximum of 18000 amps. For its low current operation, we use it for houses, commercial purposes, and also for industrial purposes.
The flow of abnormal electric current either over-current or short circuit current may cause the MCB to open or trip the circuit automatically and stop the flow of abnormal current, for protecting electrical equipment.
Electrical Symbols for MCB
The standard symbols or designs to denote the MCB.
Construction of MCB.
The outer body, of the MCB, provides mechanical strength and it also acts as an insulated housing. All sensible components of the MCB's inside the enclosure. The size of the MCB is tiny because of its less operating current.
The design MCB is available in both AC and DC. The cost of AC MCB is very less when compared with DC MCB.
MCB components.
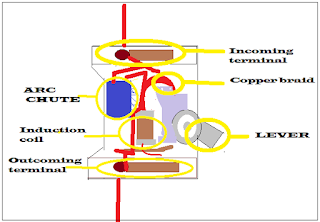
MCB comprises eight major components that are incoming terminal, arc-chute, contact point, a bimetallic strip, On-Off lever switch, magnetic coil, copper braid, and outgoing terminal.
- Incoming terminal
The incoming terminal connects to the incoming circuit. The incoming terminal receives the power and provides the path for the current flow.
- Arc-chute
It comprises Arc-chute, to quench the arc which produces by sudden disconnection of contact.
- Contact Point
MCB comprises the fixed and movable contact. The movable contact unlatches the fixed contact automatically to disconnect the circuit at abnormal conditions.
- Bimetallic strip
Bimetallic strips are made up of copper and steel. Because of the flow of high current, the temperature of the bimetallic strip expands and unlatches the spring-operated contact point.
In simple bimetallic strip provides a delayed thermal tripping mechanism for overload protection.
- Operating handle
The operating handle of MCB is called an On-Off lever switch, which helps us to operate MCB manually. The position of the lever shows whether the MCB is in 'on' or 'off' condition.
- Magnetic coil
A magnetic coil is an electromagnetic coil which is spiral and located inside the MCB to induce the magnetic field. This magnetic coil provides a magnetic tripping mechanism for short-circuit protection.
- Copper braid
A copper braid connected in series to the magnetic coil and the metallic strip. The current reaches the metallic strip through the copper braids.
- Outgoing terminal
The outgoing terminal is the last part of the MCB which sends the power to the electrical equipment.
Operation of MCB.
The MCB stops the flow of faulty current.
Normal operation.
- At normal operating conditions, the circuit breaker can be switched on manually.
- The movable contact of the MCB touches the static contact and provides the path for the flow of electric current.
- Movable contact sends the current to the induction coil.
- Then the induction coil diverts the current to the metallic strip.
- Through a metallic strip, the current travels to the outgoing terminal and leave the MCB.
Abnormal operation.
- Whenever the current flowing on the circuit exceeds the rated current for a long time, then the incoming terminal of the MCB sends the current to the induction coil.
- This over-current causes the magnetic coil to induce a magnetic field on the bimetallic strip.
- Because of the thermal effect of the magnetic field, the bimetallic strip slightly deflects downward direction.
- The copper braid pulls down the On-off lever switch and disconnects the contact points of the MCB.
How many types of MCB? What is the difference
There are two types of MCB i) Alternating current MCB ii) Direct current MCB.
AC MCB
- AC MCB is used to protect the AC application.
- The rated voltage of AC MCB is 160V to 240V.
DC MCB
- DC MCB is used to protect the DC applications.
- The rated voltage of DC MCB is 120v-1000v.
- DC current is very hard to break.
Types based on its pole
Mcb types can be divide into a single pole MCB-SP, Double pole MCB-DP, three pole MCB-TP, and four poles MCB-FP.
- Single pole MCB
Single pole MCB can control only one live or phase wire, which means single-pole MCB used to disconnect one phase or live wire from the connected device.
What is the range of current rating of single-pole M.C.B commercially available?
- Voltage range between 120v to 250 volts
- Current rating between 5 Amps to 32 Amps
- Single pole neutral MCB
SPN MCB comprises two poles, we can use one pole for phase wire disconnection, and another one for neutral wire disconnection.
In case of failure of electrical application, the single-pole neutral MCB will prevent the return current by disconnecting the neutral and a neutral wire.
- Double pole MCB
The double pole MCB comprises a two-pole. We can use these two poles for the phase to phase and also for the phase to neutral wire.
- Triple pole MCB
Triple pole MCB or three-pole mcb comprises three poles where the 3-phase line (R, Y, B) connected on mcb to disconnect 3 live lines at the same time.
- Tri-pole neutral MCB.
Tri pole neutral MCB comprises 3 poles plus 1 neutral pole.
- Four pole MCB
Four pole MCB comprises 4 poles as same as tripole neutral mcb, 3 poles correspond to 3 phases and 4 the pole corresponds to neutral.
A different trip characteristic curve of MCB
What is called an MCB trip characteristic?
The trip characteristic curve explains as "At what current MCB going to trip" and "How much time it was going to take to trip circuit?"
For example, if MCB rated value is 10 A and its tripping current is multiple of 5 times, then MCB trips in 2 sec.
A graph can explain trip characteristics of MCB, Curve drawn between operating time, and tripping current.
Tripping current:-
The current which requires operating MCB "tripping current or operating current".
Operating time:-
Time taken by MCB to "trip" is called an operating time.
According to the differentiation in a curve, MCB can be classified into five types. This Class or Type is used to identify the tripping time and operating current of MCB.
The tripping characteristics of MCB cannot be adjustable.
Each type has its characteristics and very sensible for fault current.
- Type B
- Type C
- Type D
- Type K
- Type Z
Type-B.
- Tripping current for this MCB is 3 to 5 times of full load current.
- Operating time for class-B MCB is 0.04 to 13sec.
- We use this MCB for a purely resistive load.
Application:-
- Used for residential application.
- Used for load with small inductive components such as light.
Type-C.
- Tripping current for this "Type-C MCB" is 5 to 10 times of full load current.
- Operating time for class-B MCB is 0.04 to 5sec.
- We use this MCB for very high inductive load, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, heaters,.
Application:-
- We use this MCB in a commercial or industrial type of application.
- It is very sensible for short circuit current in the circuit.
- Used with high voltage equipment such as X-ray transformer, motors.
- We prefer it to industrial areas.
Type-D.
- Tripping current for this MCB is 10 to 20 times of full load current.
- The operating time for type-D MCB is 0.04 to 3sec.
Application:-
- The big industries use MCB (Type-D) for large motors and machinery
Type-K.
- Tripping current for this MCB is 8 to 12 times of full load current.
- The operating time for type-K MCB is less than 1sec.
- In this, the current requirement for tripping is very high, but the time taken for tripping is very less.
Application:-
- We also use it in inductive load such as motor load.
- Motor with high inrush current uses this MCB.
Type-Z.
- Tripping current for this MCB is 2 to 3 times of full load current.
- Operating time for type-Z MCB is less than >1sec.
- It is highly sensitive to faulty current and the time took to trip is also less than 1 sec.
Application:-
- A highly sensitive electronic component such as semiconductor devices uses MCB.
- It used in automation industries, such as PLC and SCADA